Galium
aparine L.
Standardized Common
Name: Cleavers
Other Common Names: Bedstraw, Clivers,
Goosegrass
Family: Rubiaceae
Taxonomy: Galium
includes about 300 species, mostly Eurasian but distributed nearly worldwide. Galium
aparine, which belongs to Sect. Kolgyda, is a variable weed with a
broad range. Galium spurium L., another widespread weed, is sometimes lumped into G. aparine, and there is
considerable morphological overlap between the two. A third very similar plant,
formerly called Galium vaillantii DC., resembles G. spurium
except in having seeds with hooked bristles, like G. aparine. It is
usually lumped into G. aparine, or into G. spurium if the latter
is treated as a separate species, as G. spurium f. vaillantii
(DC.) R. J. Moore. It is in fact more common than the naked-seeded form of G.
spurium, and except for flower color is difficult to separate from G.
aparine.
Description: Annual herb. Stems
(10–)80–180 cm long, scrambling, branching at nodes, quadrangular with central
hollow, dark green to brown; ridges bearing stiff retrorse bristles, pubescent
especially at nodes. Leaves in whorls of (6–)8(–10), oblanceolate, (1–)3–6(–7)
cm long, 2.5–5(–8) mm broad, with 1 visible vein; apex cuspidate; margins
somewhat revolute; margins and often midvein beneath with tiny reverse-pointing
prickles; upper surface bearing small bristles with hooked ends. Inflorescences
cymose, bracteate, (1–)3–5(–7)-flowered; flowers pedicellate. Flowers
(1–)1.5–2(–3.5) mm broad, whitish; sepals absent; corolla rotate; petals 4,
with acute apices, sometimes pubescent; stamens 4. Fruit a schizocarp of 2
mericarps, separating at maturity, ovoid, (2–)3–4(–5) mm long, often
purplish-tinged, with dense white hooked bristles, very rarely glabrous.
Parts
in Commerce:
Whole herb
Identification:
Stems
- Quadrangular in
cross-section
- Bearing tiny
backward-pointing prickles, usually pubescent at nodes
Leaves
- Mostly 8 per
whorl, sometimes 6–10, not 4
- Margins with
tiny backward-pointing prickles
- Oblanceolate,
mostly <3 mm wide, mostly >3 cm long at maturity
- One main vein
from base, not three
- Upper surfaces
sparsely hairy with small stiff hairs, not glabrous
- Apex acute or
apiculate, not obtuse nor awned
- Taste bitter
Flowers
- Flowers borne on
pedicels
- Corolla
(1–)1.5–2(–3.5) mm in diameter, disk-shaped, not cup-shaped or funnelform
- Corolla white
- Corolla lobes 4,
acute but not apiculate
Fruits
- With pale hooked
bristles, very rarely smooth (smooth fruits usually belong to G.
spurium), never pubescent with straight hairs
- Ovate, rounded
but not spherical
- Not >5 mm
long; usually <3 mm long in G. aparine in the strict sense
- Pedicels
spreading apart after flowers mature, bent just below fruit but not bent
back along their entire length
The following table presents characters that are
said usually to distinguish among G. aparine, G. spurium, and Galium
spurium f. vaillantii (DC.) R. J. Moore, but natural variation
appears to be more complex and less easily defined. This may indicate that these
different forms would be better interpreted as belonging to a single species
complex than as being distinct species.
|
|
Galium aparine in the strict sense
|
Galium spurium
|
Galium
spurium f. vaillantii
|
|
Flower diameter
|
usually 1.5–2 mm
|
1–1.5 mm
|
1–1.5 mm
|
|
Flower color
|
white
|
greenish-yellow
|
greenish-yellow
|
|
Fruit size
|
3–5 mm
|
1.5–3 mm
|
1.5–3 mm
|
|
Fruit pubescence
|
hooked spines; rarely smooth
|
smooth
|
hooked spines
|
|
Maximum leaf size
|
6(–7) cm X 8 mm
|
4 cm X 4 mm
|
4 cm X 4 mm
|
Adulterants: Adulteration is not reported to be a problem. Of the several other
species having commercial value, G. verum L. (Lady’s Bedstraw) and G.
odoratum (L.) Scop. (Sweet Woodruff) are most similar to G. aparine,
as the leaves have a single main vein and are usually borne in whorls of at
least 8. They can, however, be distinguished by a number of features:
|
|
G. verum
|
G. odoratum
|
|
Stem shape in cross-section
|
Round with 4 faint ridges
|
Quadrangular, sturdy
|
|
Stem pubescence
|
Finely pubescent; without thick waxy coating or
downward-pointing prickles
|
Almost hairless except at nodes; without prickles
|
|
Leaf size
|
1.5–4 cm long, <3 mm broad
|
1.5–5 cm long, 4–14 mm broad
|
|
Leaf margins
|
More or less revolute
|
With minute hairs pointing toward apex (not base)
of leaf
|
|
Leaf surfaces
|
Upper surface shiny, turning dark when dried;
lower surface hairier
|
Sometimes with tiny stiff hairs on midrib,
otherwise nearly glabrous
|
|
Leaf apex
|
Acute or perhaps mucronulate
|
With sharp membranous point
|
|
Inflorescence
|
Short-branched, many-flowered panicle
|
Lax panicle with reduced bracts
|
|
Corolla size and shape
|
Disk-shaped, 2–3.5 mm in diameter
|
Funnelform, at least 4 mm in diameter
|
|
Corolla color
|
Yellow
|
White
|
|
Fruit
|
Ovoid, <1.5 mm long, hairless or occasionally
pubescent
|
Ovoid, 2–3 mm long, with strong hooked bristles
|
References:
British Herbal Medicine
Association. British Herbal Pharmacopoeia. BHMA; 1996:59–60.
Ehrendorfer F. Rubiaceae. In: Tutin TG, Heywood VH, Burges NA, et al.,
eds. Flora Europaea. Vol. 4. Cambridge: Cambridge University
Press; 1976:14–36.
Fernald ML. Gray’s Manual of Botany, 8th ed. New York: American Book
Company; 1950:1319–1326.
Lawson CA. The Genus Galium (Rubiaceae) in
the Southeastern United States. Ph.D. Dissertation, University of Oklahoma;
1976.
Malik N, Vanden Born WH. The biology of Canadian
weeds. 86. Galium aparine L. and Galium spurium L. Canad J Pl
Sci. 1988;68:481–499.
Moore RJ. The Galium aparine complex in
Canada. Canad J Bot. 1975;53:877–893.
Pötter U, Klopfer K. Mehrdimensionale Varianzanalyse
zur Artentrennung von Galium aparine L. und Galium spurium L. Feddes
Repert. 1990;101:257–262.
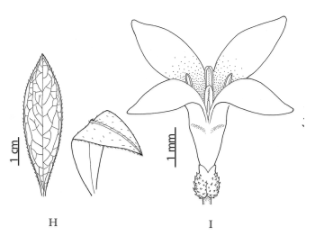
Figure
29: a–d, Galium aparine leaf, habit, flowers and
fruit; e–g, G. verum leaf, flower and
fruit; h–j, G. odoratum leaf, flower
and fruit.