Issue:
123
Page: 62-73
Herbal Supplement Sales in US Increased by 9.4% in 2018
by Tyler Smith,a Michelle Gillespie,b Veronica Eckl,b Claire Morton Reynoldsc
HerbalGram.
2019; American Botanical Council
a American Botanical Council; Austin, Texas
b SPINS; Chicago, Illinois
c Nutrition Business Journal; Boulder, Colorado  Click here for PDF of article Click here for PDF of article
Herbal supplement sales in the United States experienced record growth in 2018, increasing by an estimated 9.4% from 2017, according to the Nutrition Business Journal (NBJ). Consumers spent a total of $8.842 billion on herbal supplements across all market channels in 2018 — an increase of roughly $757 million in sales from the previous year. This marks the strongest US sales growth of herbal supplements since 1998.1
The sales estimates in this report are based on US retail sales data provided by SPINS, a market research firm based in Chicago, Illinois, and NBJ, a Boulder, Colorado-based publication of the New Hope Network, an Informa media company that is focused on the natural products industry. NBJ provided estimates of total herbal supplement sales in the United States, as well as sales broken down by retail channel (mass market, natural and health food, and direct sales) and product type (single-herb supplements vs. combination formulas). SPINS provided sales data for the 40 top-selling herbal and fungal ingredients in both mainstream and natural retail channels. In previous years, SPINS collaborated with IRI, a market research firm also based in Chicago, to determine total mainstream sales for the 40 top-selling herbs. However, the database previously used by IRI was discontinued and, therefore, the mainstream sales figures in this report reflect data provided by SPINS only.
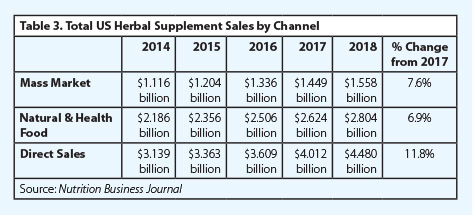
In addition to the strong overall sales growth for herbal dietary supplements in 2018, total retail sales increased in each of the three market channels monitored by NBJ in 2018. For the second year in a row, direct sales of herbal supplements experienced the strongest growth, increasing by 11.8% to a total of $4.480 billion in 2018. NBJ’s mass market channel experienced the second strongest growth in 2018, reaching a total of $1.558 billion, an increase of 7.6% from the previous year. Finally, herbal supplement sales in natural and health food stores totaled $2.804 billion in 2018, according to NBJ, an increase of 6.9% from 2017.
The SPINS sales data for individual herbs and fungi discussed in this report reflect sales of dietary supplements in which that herb or fungus is the primary functional ingredient. This includes only products that meet the legal definition of a dietary supplement per the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA).1 The figures in this report reflect the most current estimates (as of July 2019) for herbal dietary supplement sales during the 52-week period ending December 30, 2018. Sales figures are for dietary supplement products only and do not reflect sales of herbal teas or cosmetics with botanical ingredients.
Supplements for Immune Health and Weight Management Drive Mainstream Retail Sales
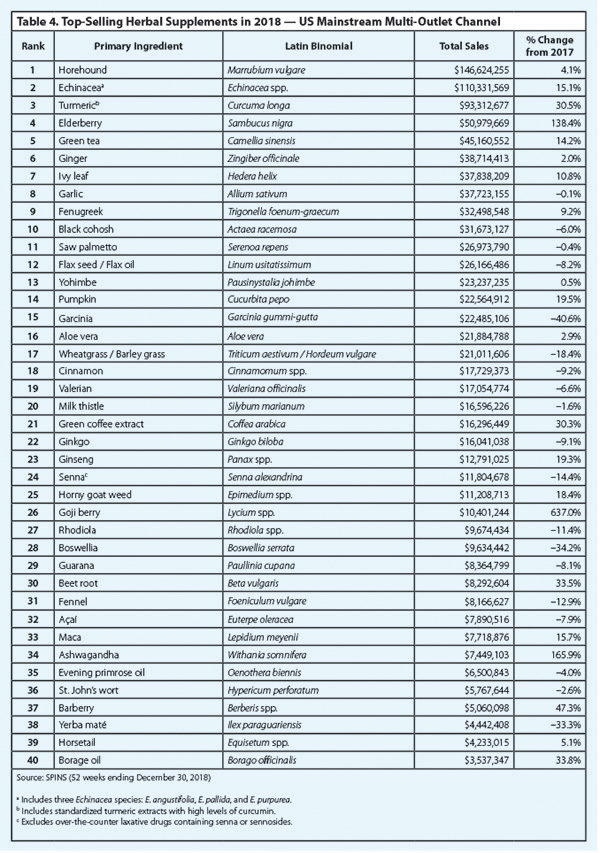
Among the top-selling herbal dietary supplements in mainstream US retail outlets, products with horehound (Marrubium vulgare, Lamiaceae) listed as the primary ingredient have grossed the highest sales each year since 2013, and this remained true in 2018. Sales of horehound supplements totaled $146,624,255 in 2018, a 4.1% increase in sales from 2017. Horehound, a member of the mint family, has bitter properties and has been used traditionally for respiratory issues, such as cough and colds, and, less commonly, for digestive conditions, such as stomachache and intestinal worms.2 As a dietary supplement, horehound is now most commonly found in cough drop and lozenge preparations.
Goji (Lycium spp., Solanaceae) berry supplements experienced the strongest growth in the 2018 mainstream channel, with sales increasing 637% from 2017. Sales of goji berry totaled $10,401,244 in 2018, making it 26th top-selling supplement ingredient in this channel. Goji berry first appeared among the top 40 herbal supplements in the mainstream channel in 2015 during the so-called “superfood” craze. Mainstream sales of the ingredient declined in 2016 and 2017 as the market became saturated with a variety of “new” superfoods, but goji berry experienced a resurgence in popularity in 2018.
According to SPINS, the top-selling goji berry products in the 2018 mainstream channel were marketed for weight loss. Twenty percent of all supplement users in the United States purchased products marketed for weight loss in 2018, according to the Council for Responsible Nutrition’s (CRN’s) 2018 Consumer Survey on Dietary Supplements. However, only supplement users in the 18- to 34-year-old age group listed weight loss as one of the six primary reasons for taking supplements.3 As noted in previous HerbalGram market reports, consumers are increasingly choosing products for weight management, as opposed to weight loss, with the goal of improving health in general. Overall health and wellness remained the top health reason for consumers to take supplements across all age groups in 2018, CRN’s report noted.3
Besides goji berry, three other ingredients on the top 40 list had mainstream sales increases greater than 40% in 2018 (based on dollar volume): ashwagandha (Withania somnifera, Solanaceae), elderberry (Sambucus nigra, Adoxaceae), and barberry (Berberis spp., Berberidaceae). 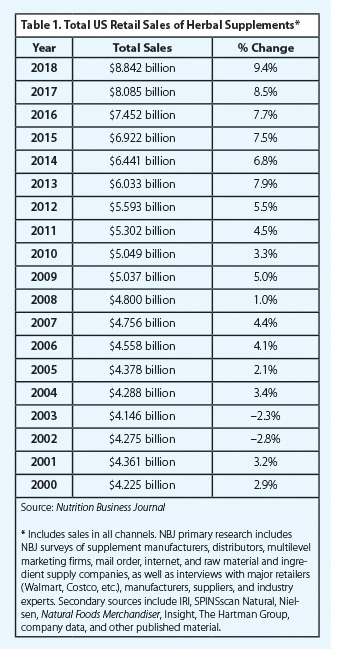
For the first time, strong sales of ashwagandha supplements in mainstream retail outlets earned the herb a spot among the 40 top-selling ingredients in this channel. Mainstream ashwagandha sales in 2018 increased 165.9% from the previous year, with sales totaling $7,449,103. Ashwagandha has been one of the 40 top-selling ingredients in natural retail stores since 2015, but its appearance among the top 40 herbs in the mainstream channel in 2018 suggests more widespread familiarity among casual consumers of natural products. Mainstream ashwagandha sales in 2018 likely benefitted from the continued popularity of ingredients traditionally used in Ayurveda, the primary traditional medical system of India. Turmeric (Curcuma longa, Zingiberaceae), another popular Ayurvedic ingredient, which experienced the largest mainstream sales increase in 2017, had a 30.5% increase in sales from 2017 and ranked third in 2018.
Elderberry sales also saw strong growth in 2018, increasing by 138.4% from 2017 to a total of $50,979,669, making it the fourth top-selling ingredient in this channel. Rising sales of elderberry, which is commonly found in products marketed for immune health, may have been related to the unusually severe flu activity reported for the 2017-2018 season in the United States. According to the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, the 2017-2018 season was one of the longest flu seasons in recent years and the first to be ranked as “high severity” in all age groups.4 Several ingredients typically sold for immune health benefits performed well across both market channels in 2018. In the mainstream channel, echinacea (Echinacea spp., Asteraceae) and ivy leaf (Hedera helix, Araliaceae), for example, saw increases of 15.1% and 10.8%, respectively. 
Barberry, another ingredient new to the mainstream top 40 list in 2018, saw the only other increase greater than 40% among the top 40 ingredients in 2018 (by dollar volume). Sales of barberry increased by 47.3% from 2017, totaling $5,060,098. According to SPINS, many of the top-selling barberry supplements were marketed for their berberine content and liver support benefits. Berberine is an alkaloid found in several plants, including goldenseal (Hydrastis canadensis, Ranunculaceae) and Oregon grape (Berberis aquifolium, Berberidaceae), among others. In vitro studies have found that berberine exhibits anti-inflammatory and antioxidant activities, and results from human clinical trials suggest that it may be useful for lowering blood lipids and blood glucose and improving insulin resistance.5 In addition, a recent meta-analysis of six randomized clinical trials concluded that berberine may have positive effects on liver function and for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, but the authors recommended additional, higher-quality studies to confirm these potential benefits.6
The only ingredient on the top 40 list that experienced a decrease in mainstream sales of more than 40% in 2018 was garcinia (Garcinia gummi-gutta, Clusiaceae). Sales of garcinia fruit preparations totaled $22,485,106 in 2018, a 40.6% decrease from 2017. Despite falling sales, garcinia supplements still ranked 15th in overall sales in the mainstream channel. Although sales of other herbal ingredients typically marketed for weight loss tended to perform well in 2018, garcinia’s claimed weight-loss benefits may have been overshadowed by negative media coverage. In July 2018, for example, popular daytime talk show host Dr. Mehmet Oz settled a case for $5.25 million in which plaintiffs alleged that he promoted garcinia as a “magic weight-loss cure” with no supporting scientific evidence.7
As HerbalGram’s annual market reports generally focus on specific herbs and fungi, certain ingredients are excluded from the top 40 list each year. Three products that would have appeared on the 40 top-selling ingredients list in the US mainstream channel were removed: “bee products (not propolis),” “Ayurvedic herbs (other),” and Relora® (InterHealth Nutraceuticals/Lonza; Benicia, California). Although bee products (e.g., pollen, royal jelly, etc.) are considered natural products, HerbalGram chose not to include this category of ingredients as they are neither herbs nor fungi. If non-propolis bee products had remained on the list, they would have ranked 13th in overall sales. Ayurvedic herbs (other) also was excluded due to its lack of specificity. Had it remained on the list, it would have ranked 37th in total mainstream sales in 2018, after excluding non-propolis bee products. Finally, as the only branded supplement on the list, Relora, a combination formula containing bark extracts of magnolia (Magnolia officinalis, Magnoliaceae) and phellodendron (Phellodendron amurense, Rutaceae), also was removed from the report. Had it been included, Relora would have ranked 39th in total overall mainstream sales, after excluding non-propolis bee products and Ayurvedic herbs (other).
 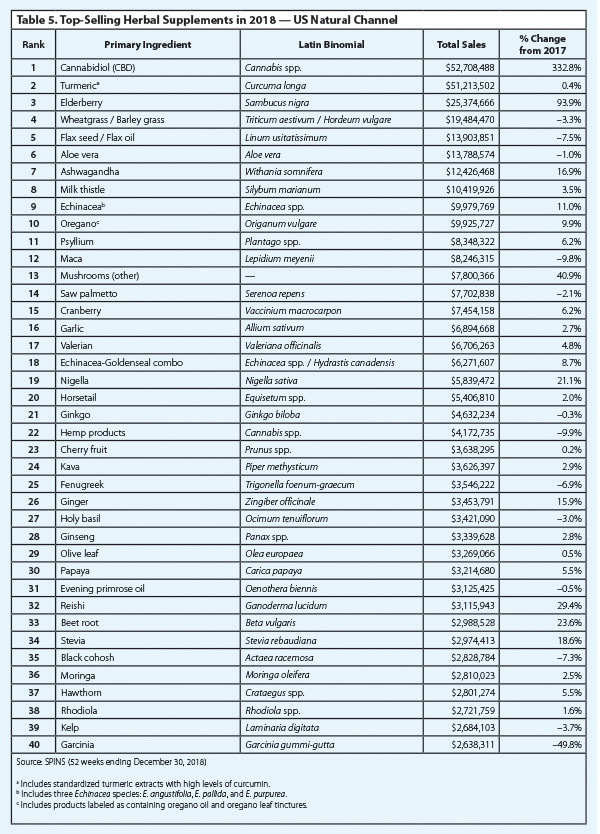
CBD and Mushroom Supplements Experience Significant Growth in Natural Retail Channel
Since 2013, turmeric has been the top-selling herbal dietary supplement ingredient in natural retail stores in the United States. But, in 2018, skyrocketing sales of cannabidiol (CBD), a psychoactive but nonintoxicating constituent of Cannabis sativa (Cannabaceae), made it not only the top-selling ingredient in the natural channel but also the fastest-growing. SPINS has been tracking sales of CBD since 2016, but it made its first appearance on the natural channel’s top 40 list in 2017 as the 12th top-selling ingredient, with a 303% increase in sales from the previous year. In 2018, CBD sales totaled $52,708,488 — a 332.8% increase from 2017.
According to SPINS, roughly 60% of the CBD products sold in the US natural channel in 2018 were in the form of alcohol-free tinctures, followed by capsules and softgels. The vast majority of the CBD products were marketed for “non-specific health focuses,” with mood support and sleep as the next most-popular uses.
Although CBD products have been sold online and in stores for years, the federal regulatory situation remains complicated. SPINS explained that the CBD supplements included in the natural channel data are products that contain CBD extracted from the aerial parts of hemp — an important legal distinction. Upon the passage of the 2018 Farm Bill, the FDA removed hemp (defined as any Cannabis sativa plant “with a delta-9 tetrahydrocannabinol [THC] concentration of not more than 0.3 percent on a dry weight basis”) from the Controlled Substances Act (CSA). However, any Cannabis sativa plants (or parts/derivates thereof) with a THC concentration above 0.3% (defined as “cannabis” or “marihuana”) remain Schedule I substances under the CSA.8
Still, as of July 2019, the FDA does not consider CBD, regardless of its origin, to be a legal dietary supplement ingredient under section 201(ff)(3)(B) of the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic (FD&C) Act, according to its website.8 The FDA has noted that “if a substance (such as … CBD) is an active ingredient in a drug product that has been approved under section 505 of the FD&C Act [21 U.S.C. § 355], … then products containing that substance are excluded from the definition of a dietary supplement.” In a Q&A on its website, the FDA explains that CBD is the main active ingredient in Epidiolex® (GW Pharmaceuticals; Salisbury, UK), which the FDA approved in June 2018.9 Despite this, CBD products have flooded the US marketplace, and sales show no signs of slowing.
Although sales of CBD products increased significantly in 2018, sales of hemp products declined by 9.9%. According to SPINS, the majority of supplements in this category are hemp seed oils that contain a negligible amount of CBD and typically are marketed for their omega-3 fatty acid content. The reason for the sales decline is unclear, but it may be due to increased availability of and consumer preference for other plant-based sources of protein and fiber.
The only other ingredients in the natural channel with sales increases greater than 40% in 2018 were elderberry (93.9%), discussed previously, and “mushrooms (other).” SPINS tracks sales of a few individual species of fungi, including reishi (Ganoderma lucidum, Ganodermataceae), chaga (Inonotus obliquus, Hymenochaetaceae), and cordyceps (Cordyceps militaris, Cordycipitaceae), while the mushrooms (other) category combines sales of multiple species, including lion’s mane (Hericium erinaceus, Hericiaceae), turkey tail (Trametes versicolor, Polyporaceae), and blends thereof. Sales of mushrooms (other) increased by 40.9% from 2017 and totaled $7,800,366 in 2018. After CBD, elderberry, and mushrooms (other), reishi had the fourth highest percent sales increase in 2018 in the natural channel among the top 40 ingredients, with a 29.4% increase from the previous year.
According to SPINS, mushrooms (other) were primarily sold in the form of vegetable capsules and powders. Many of the top mushroom products in this category listed immunity or cognitive health as main health focuses, followed by non-specific uses. Sales of mushroom products marketed for immune health may have increased in part due to the extended 2017-2018 flu season.
In its annual food trends forecast, Whole Foods Market correctly predicted that functional mushrooms would be a top-seller during 2018.10 Similarly, in its “Top 10 Trends Predictions for 2018,” SPINS projected that adaptogens would see increased growth in 2018 and that there would be “continued (and progressively innovative) applications of functional mushrooms across food, beverages, and dietary supplements, plus the integration of other ingredients that focus on adaptogenic properties.”11 In general terms, an adaptogen is a substance that improves the body’s ability to adapt to stress, although various definitions exist.12 In 2018, functional mushrooms with claimed adaptogenic properties increasingly were incorporated into a range of products, including chocolates, coffee, and cosmetics.13
As in the mainstream channel, the only top 40 ingredient that experienced a sales decrease of more than 40% in the natural channel was garcinia. Sales of garcinia supplements in natural retail outlets decreased by 49.8% from 2017 to 2018, during which time it dropped from the 20th top-selling ingredient to the 40th top-selling ingredient.
HerbalGram chose to exclude three ingredients originally in the top 40 list in the natural channel: spirulina (Arthrospira platensis and A. maxima, Microcoleaceae) and chlorella (Chlorella vulgaris, Chlorellaceae), which are classified as cyanobacteria and algae, respectively, and arginine, an amino acid. Had it remained on the list, spirulina would have ranked 11th in total overall sales in the 2018 natural channel. Chlorella would have ranked 20th (after excluding spirulina), and arginine would have ranked 31st (after excluding spirulina and chlorella).
Direct Sales
For the second year in a row, percent sales growth of herbal supplements in the direct sales channel was higher than the percent sales growth in the mass market and natural and health food channels, according to NBJ’s estimates. Sales in this market channel grew by 11.8% from 2017 and totaled $4.480 billion in 2018. The direct sales channel includes multilevel marketing companies (also known as network marketing companies), mail- and internet-order sales companies, direct-response TV and radio sales, and sales by health practitioners.
Single-Herb Supplements vs. Combination Formulas
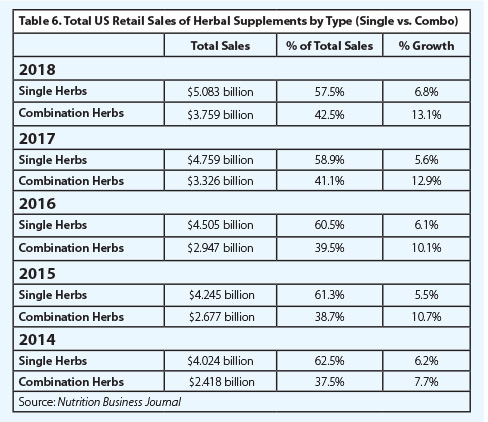
Since 2011, sales of combination formulas (multi-herb supplements) have grown faster, by percentage, than that of single-herb supplements. This was the case once again in 2018, with sales of combination formulas and single-herb supplements increasing by 13.1% and 6.8%, respectively. Combination formulas typically include multiple herbs designed to work additively and/or synergistically to support a particular health function (or functions), while single-herb supplements often are intended for a variety of uses. Although single-herb supplements have composed the majority of total sales for more than a decade, the percentage gap between overall sales of these two product types has been closing each year.
Conclusion
Total sales of herbal supplements in the United States have increased each year since 2004, with sales of these products more than doubling during this period. Increasingly, US consumers are gravitating toward plant-based products that they perceive as safe, natural, and effective options to help maintain health and wellness. Perhaps not surprisingly, herbal supplements experienced stronger percent sales growth than the dietary supplements category as a whole in 2018.14 Previously trending ingredients, such as Ayurvedic herbs and botanicals with general health benefits, continued to be top-sellers in both mainstream and natural channels in 2018, while several ingredients with newfound, widespread popularity, such as mushrooms and CBD, also fueled sales, particularly in natural retail outlets. Given that 2018 experienced the strongest overall sales growth in two decades, and the natural products industry’s ongoing focus on increased transparency and self-regulation efforts, consumer trust in herb- and fungi-based products appears to remain strong.
References
- Blumenthal M, Cavaliere C, Ferrier GKL. Total sales of herbal supplements in United States show steady growth. HerbalGram. 2006;71:66. Available at: http://cms.herbalgram.org/herbalgram/issue71/article3012.html. Accessed August 12, 2019.
- Horehound. Purdue University Horticulture & Landscape Architecture website. Available at: https://hort.purdue.edu/newcrop/med-aro/factsheets/horehound.html. Accessed August 12, 2019.
- 2018 CRN Consumer Survey on Dietary Supplements. Council for Responsible Nutrition website. Available at: www.crnusa.org/CRNConsumerSurvey. Accessed August 12, 2019.
- Influenza (flu): 2017-2018. US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention website. Available at: www.cdc.gov/flu/about/season/flu-season-2017-2018.htm. Accessed August 12, 2019.
- Cicero AF, Baggioni A. Berberine and its role in chronic diseases. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2016;928:27-45. Available at: www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27671811. Accessed August 12, 2019.
- Wei X, Wang C, Hao S, Song H, Yang L. The therapeutic effect of berberine in the treatment of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a meta-analysis. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2016. doi: 10.1155/2016/3593951. Available at: www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4947506/. Accessed August 12, 2019.
- Edelstein JS. Dr. Oz prescribes $5.25M settlement in false ad case. Lexology website. Available at: www.lexology.com/library/detail.aspx?g=699ce0d5-0508-450a-b620-968f4e238bc2. Accessed August 12, 2019.
- FDA regulation of Cannabis and Cannabis-derived products: questions and answers. US Food & Drug Administration website. Available at: www.fda.gov/news-events/public-health-focus/fda-regulation-cannabis-and-cannabis-derived-products-questions-and-answers#othercbdapproved. Accessed August 12, 2019.
- FDA approves first drug comprised of an active ingredient derived from marijuana to treat rare, severe forms of epilepsy [press release]. Silver Spring, MD: US Food and Drug Administration; June 25, 2018. Available at: www.fda.gov/NewsEvents/Newsroom/PressAnnouncements/ucm611046.htm. Accessed July 5, 2018.
- Our 2018 food trends forecast: lavender lattés, mushroom cocoa, vegan tuna and more. December 28, 2017. Whole Foods Market website. Available at: www.wholefoodsmarket.com/blog/our-2018-food-trends-forecast-lavender-lattes-mushroom-cocoa-vegan-tuna-and-more. Accessed August 12, 2019.
- Top 10 trend predictions for 2018. SPINS website. Available at: www.spins.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/01/TrendWatch-2018TrendPredictions.pdf.
- Panossian A, Wagner H. Adaptogens: a review of their history, biological activity, and clinical benefits. HerbalGram. 2011;90:52-63. Available at: http://cms.herbalgram.org/herbalgram/issue90/Feat_Adaptogens.html. Accessed August 12, 2019.
- Judkis M. Mushrooms are turning up in coffee, chocolate, even beauty ‘dusts.’ How come? The Washington Post. February 21, 2018. Available at: www.washingtonpost.com/news/voraciously/wp/2018/02/21/mushrooms-are-turning-up-in-coffee-chocolate-even-beauty-dusts-how-come/. Accessed August 12, 2019.
- Morton C. By the numbers: the state of the natural products industry. January 6, 2019. New Hope Network website. Available at: www.newhope.com/business-resources/numbers-state-supplement-industry. Accessed August 12, 2019.
|